10 Tools Every Software Developer Should Master in 2026
Discover the 10 essential tools every software developer must master in 2026. Boost productivity, security, collaboration, and AI-driven workflows with this ultimate dev stack guide.

In the ever-evolving landscape of software engineering, mastering the right set of developer tools is no longer optional—it's a necessity for productivity, career growth, and building robust, modern applications.
The right toolkit shapes your programming productivity, shields your projects from security vulnerabilities, and unlocks your potential for innovation in collaborative teams.
This comprehensive guide covers the 10 essential developer tools every engineer should master, from foundational technologies to cutting-edge AI-powered solutions.
The Business Case for Tool Mastery
- 30-40% productivity improvement through proper tool selection and proficiency
- Reduced bug rates via integrated security scanning and automated testing
- Faster onboarding for new team members with standardized tooling
- Better collaboration through unified communication and version control
Key Trends in Developer Tools for 2026
AI and Automation in Software Development
AI coding assistants like Cursor and GitHub Copilot have become central to programming productivity, offering advanced capabilities from instant code generation to full-stack test automation. This enables developers to focus on higher-level logic and solution design.
Automation now accelerates CI/CD pipelines, code reviews, and pull request documentation, allowing teams to ship reliably at scale. AI-powered security scanning and threat modeling have reduced manual code review overhead by up to 50%.
Cloud-First and Remote Development Workflows
Remote development isn't just a trend—it's the new mainstream. Platforms like GitHub Codespaces, VS Code Remote, and Dockerized environments provide seamless remote setups with robust collaboration and consistent environments across teams.
Security and Compliance Escalation
With software supply chains under increasing threat, security has escalated to a primary engineering concern. The OWASP 2026 risk framework highlights critical vulnerabilities in code dependencies and AI-powered endpoints.
Proactive adoption of automated security testing (SAST/DAST), software composition analysis (SCA), and SBOM (Software Bill of Materials) solutions are now integral to safe releases and regulatory compliance.
Multi-Language and Framework Diversity
Developers increasingly work across JavaScript, Python, Go, Rust, and other languages with frameworks like React, Next.js, and Spring. Modern IDEs and AI coding assistants have adapted with plugins and extensions to bridge language gaps and support polyglot projects seamlessly.
10 Essential Developer Tools Overview
1. Git & Git-Flow Branching Model
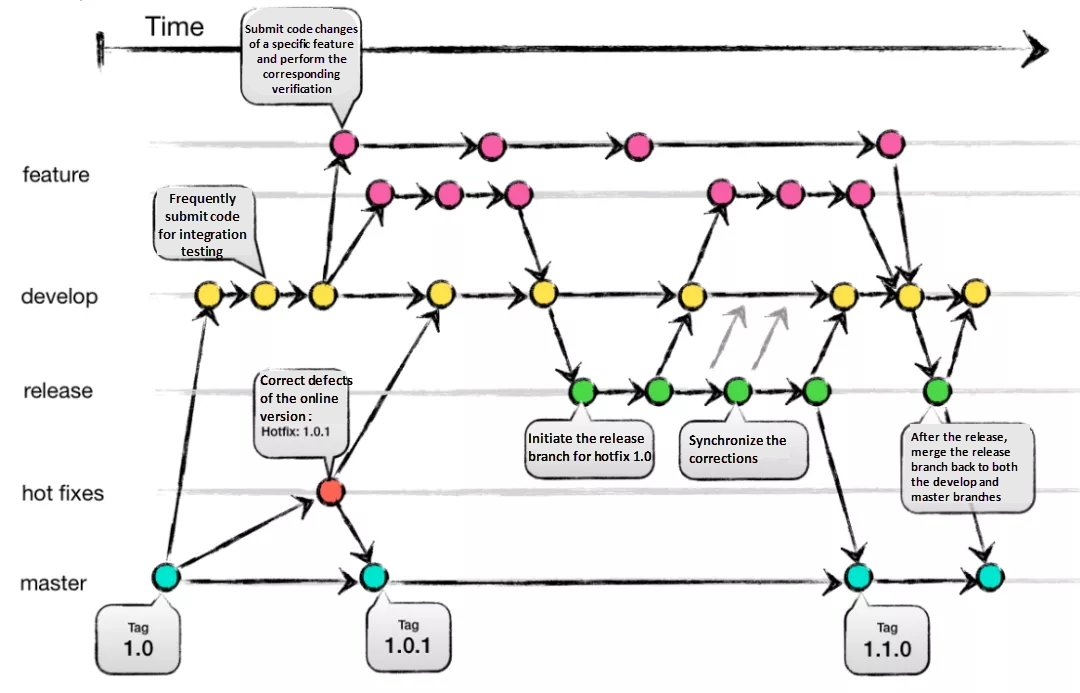
Primary Use: Distributed version control and team collaboration
Git remains the gold standard for source code management. Mastery of Git—combined with structured branching models like Git-Flow—directly impacts project stability, team collaboration, and development velocity.
Why It Matters:
- Distributed collaboration: Every developer maintains a full repository copy
- History tracking: Complete audit trail of changes for root-cause analysis
- Branching flexibility: Feature, release, and hotfix branches minimize deployment risk
- CI/CD integration: Git webhooks trigger automated testing and deployment pipelines
Key Git-Flow Strategy:
main/master: Production-ready code onlydevelop: Integration and testing branchfeature/: Isolated feature developmentrelease/: Staged releases for QA and bugfixeshotfix/: Critical production fixes
Best Practices for Git Mastery:
- Keep pull requests (PRs) small and focused (200-400 lines maximum)
- Write descriptive commit messages following conventional commit standards
- Integrate frequently and address merge conflicts early
- Enforce code review policies automated via CI checks
- Document your branching model for team discoverability
Real-World Impact: Teams using structured Git-Flow report 40% faster merge cycles and 25% fewer production incidents.
2. VS Code / IntelliJ IDEA
Primary Use: Advanced code editing and debugging
World-class code editors remain the primary touchpoint for developer productivity, directly impacting your daily efficiency.
VS Code Strengths:
- Lightning-fast performance and minimal resource usage
- Free and open-source with massive extension ecosystem (50,000+ extensions)
- Built-in terminal, Git support, and browser-based Codespaces
- Seamless AI integration with Copilot, Cursor, and other coding assistants
- Remote development: SSH, containers, and Kubernetes environments
IntelliJ IDEA Advantages:
- Deep code intelligence with superior static analysis
- Powerful refactoring tools (rename, extract method, optimize imports)
- Native JVM support for Java, Kotlin, Scala with tight build integration
- Advanced debugging with breakpoints, watch expressions, and memory profiling
- Enterprise plugin ecosystem for frameworks, Docker, Kubernetes, and Jira
Essential Extensions & Integrations:
| IDE | Must-Have Extensions | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| VS Code | Prettier, ESLint | Code formatting and linting |
| Remote - SSH/Containers | Remote development environments | |
| Docker, Kubernetes | Container orchestration | |
| GitLens | Advanced Git visualization | |
| IntelliJ IDEA | Snyk, SonarLint | Security vulnerability scanning |
| Docker, Kubernetes | Container management | |
| Jira, GitHub | Project management integration |
Optimization Tips:
- Sync settings to cloud (Settings Sync in VS Code, Account in IntelliJ)
- Create workspace templates for repeatable project setups
- Leverage remote development to run code on VMs/containers
- Customize keyboard shortcuts for your workflow
- Use multi-cursor editing for batch changes
3. Cursor AI Assistant

Primary Use: AI-powered code completion and intelligent refactoring
Cursor AI represents the next generation of coding assistants, dramatically accelerating development velocity through context-aware intelligence.
Core Capabilities:
- Context-aware completions: Generates idiomatic code for 20+ languages
- Multi-file refactoring: Rename variables, extract functions across entire codebases
- YOLO Mode: Autonomous code changes with automatic validation
- Composer mode: Break large tasks into AI-powered substeps
- Code explanation: Understand legacy code through AI-generated documentation
Performance Benchmarks:
- 35% faster task completion compared to manual coding
- 45% reduction in bugs through integrated test generation
- Outperforms competitors in context handling for verbose prompts
YOLO Mode: A Game-Changer:
YOLO mode allows bold, autonomous code changes—whether automating TDD cycles, refactoring entire functions, or rapid prototyping. Users can confidently delegate rewrites, testing, and validation to Cursor's AI engine.
Real-World Use Cases:
- ✅ Refactoring legacy code safely with automatic testing
- ✅ Onboarding to unfamiliar repositories with AI-guided navigation
- ✅ Auto-generating comprehensive unit and integration tests
- ✅ Bug fixes and documentation across distributed codebases
- ✅ API migrations with cross-repo search and validation
Pro Tips for Maximum Productivity:
- Pair YOLO mode with keyboard shortcuts for instant execution
- Leverage the instant diff/review pane before accepting changes
- Use Composer mode for multi-step refactoring tasks
- Combine with Git for easy rollback of AI-generated changes
4. Builder.io Visual CMS
Primary Use: Design-to-code workflows and headless content management
Builder.io empowers product teams to deliver high-impact frontend experiences through visual editing while maintaining code quality and flexibility.
Core Features:
- Visual drag-and-drop editing with theme and component controls
- Headless CMS integration with Next.js, Remix, React, Vue, and Qwik
- Real-time device preview across desktop, tablet, and mobile
- A/B testing and personalization for dynamic content targeting
- Figma integration: Import designs and convert to reusable code components
Design-to-Code Workflow:
- Designers create prototypes in Figma
- Builder.io imports designs automatically
- Components are converted to React/Vue/Qwik code
- Developers customize components while designers edit visually
- Zero handoff friction, rapid iteration cycles
Component Permissions & Collaboration:
- Role-based access control: Secure sensitive components
- Change tracking and rollback: Protect critical versions
- Visual editing for non-developers: Designers manage content without code
- Real-time team comments: Seamless feedback and collaboration
Integration Strategy:
Builder.io plugs into existing projects via lightweight SDKs. Existing design systems can be imported programmatically or edited visually, making migration seamless for scaling teams.
5. OWASP Security Toolkit

Primary Use: Application security scanning and vulnerability management
No developer stack is complete without robust, practical security integrated at every layer.
Critical Security Risks in 2026:
According to OWASP Top 10 2026, the leading threats include:
- Supply chain attacks on dependencies and open-source libraries
- Broken access control in APIs and microservices
- Injection attacks (SQL, command injection, AI prompt injection)
- Insecure CI/CD pipelines lacking deployment safeguards
- AI-centric vulnerabilities in generative models and LLM integration
OWASP-Recommended Tools:
| Tool | Function | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| OWASP ZAP | Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) | Runtime vulnerability detection |
| Dependency-Check | Software Composition Analysis (SCA) | Vulnerable library detection |
| Snyk | SAST/DAST/SCA automation | Integrated security scanning |
| Semgrep | Static Application Security Testing | Code pattern analysis |
| CycloneDX | Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) | Dependency inventory tracking |
| GenAI Security Project | AI model safety (NEW) | LLM vulnerability scanning |
Security Implementation Strategy:
- Integrate security in CI/CD pipelines
- Automated SAST on every commit
- Dependency scanning on pull requests
- DAST testing in staging environments
- Implement secure code review practices
- Automated security checks via Snyk/Semgrep
- Manual review for high-risk changes
- Threat modeling for new features
- Generate and maintain SBOM
- Track all open-source dependencies
- Monitor for disclosed vulnerabilities
- Meet compliance requirements (SLSA, CycloneDX)
- Adopt secure coding patterns
- Principle of least privilege in access control
- Input validation and output encoding
- Secure secrets management (HashiCorp Vault)
6. Jira / Modern Project Management Tools
Primary Use: Agile planning, sprint tracking, and workflow automation
Effective project management underpins successful dev teams and directly impacts delivery velocity.
Core Planning Capabilities:
- Kanban and Scrum boards: Visualize workflow and bottlenecks
- Custom workflows and automations: Adapt to team processes
- Blocker tracking: Identify dependencies and risks early
- Sprint planning: Time-box work and track velocity metrics
CI/CD and Git Integration:
- Native GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket integration for branch and PR tracking
- Automatic ticket transitions on branch creation/pull request merge
- Build health dashboards showing pipeline status in real-time
- Release automation: Trigger deployments from Jira tickets
Collaboration & Visibility:
- Real-time comments and mentions with threaded discussions
- Stakeholder notifications with granular visibility control
- Retrospectives: Built-in feedback capture and action items
- Burndown charts: Track sprint progress visually
Productivity Metrics:
- Velocity tracking to predict team capacity
- Lead time and cycle time for continuous improvement
- Automated burndown showing day-by-day progress
- Dashboard customization for role-specific views
7. Docker / Containerization
Primary Use: Reproducible development and production environments
Containers drive consistent, fast, and secure environments from local development through production deployment.
Why Containerization Matters:
- Eliminates "works on my machine" syndrome: Identical environments everywhere
- Enables microservices architecture: Service isolation and scaling
- Accelerates CI/CD: Faster builds and deployments
- Improves security: Container image scanning and isolation
- Supports polyglot teams: Any language/framework in same ecosystem
Local Development Setup with Docker:
text# Example: Node.js development environment
FROM node:18-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm ci
COPY . .
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["npm", "run", "dev"]
Docker Compose for Development Stacks:
Orchestrate multiple services (app, database, cache, API) with single docker-compose.yml file:
textversion: '3.8'
services:
app:
build: .
ports:
- "3000:3000"
depends_on:
- db
- redis
db:
image: postgres:15
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: dev
redis:
image: redis:7-alpine
Kubernetes for Production Orchestration:
- Scaling: Automatically scale services based on demand
- Self-healing: Restart failed containers
- Rolling updates: Zero-downtime deployments
- Service discovery: Automatic DNS for inter-service communication
Common Docker Use Cases:
- Database sandboxing: Isolated PostgreSQL/MySQL for each developer
- Service dependency simulation: Mock APIs, cache layers, message queues
- Secure ephemeral test environments: Spin up/tear down quickly
- CI/CD pipeline stages: Consistent build, test, and deployment environments
8. ITIL Process Tools
Primary Use: Service management, change control, and incident response
Service management maturity is essential for stability, compliance, and robust incident/change management in larger organizations.
Core ITIL Practices for Developers:
| Practice | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Request Fulfillment | Standardized support for routine tasks (infra setup, access requests) | Reduces manual overhead |
| Incident Management | Automated triage, escalation, on-call scheduling | Faster MTTR (mean time to resolution) |
| Change Management | Controlled, auditable deployments via code pipelines | Reduces deployment failures by 35% |
| Problem Management | Root cause analysis for recurring incidents | Prevents repeat outages |
Change Management Integration with CI/CD:
Modern ITIL tools integrate with Jira and deployment pipelines:
- Change tickets auto-created from deployments
- Approval workflows gate production releases
- Automatic rollback on failure detection
- Compliance audit trails for regulations
Leading ITIL Tools in 2026:
- ServiceNow: Enterprise-grade with deep integrations
- Jira Service Management: Seamless Jira integration for dev teams
- BMC Helix: Specialized incident and change management
- Atlassian Opsgenie: On-call scheduling and alerting
9. Emotional Intelligence and Communication Platforms
Primary Use: Team cohesion, feedback, and remote collaboration
Technology tools for empathy and psychological safety are as crucial as code tools for modern development teams.
Why Emotional Intelligence Matters for Engineers:
- Higher software quality through better collaboration
- Reduced turnover: Supportive teams retain talent
- Faster innovation: Psychological safety enables risk-taking
- Mental health: Remote work requires explicit EQ tools
- Conflict resolution: Prevents toxic team dynamics
Top EQ Tools for Development Teams:
| Tool | Function | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Officevibe | Pulse surveys, sentiment analytics | Team mood and engagement tracking |
| 15Five | Goal tracking, feedback collection | Performance reviews and 1-on-1s |
| Donut | Team building, peer matching | Schedule virtual coffee chats via Slack |
| Gather | Anonymous feedback, mediations | Conflict resolution and survey insights |
Implementation for Remote Teams:
- Weekly pulse surveys: 2-minute sentiment checks
- Peer feedback matching: Algorithmic pairing for 1-on-1 discussions
- Anonymous suggestion box: Psychological safety for candid feedback
- Mood trackers: Visual sentiment dashboards
- Guided reflection: AI-powered self-assessment prompts
10. Algorithms & Problem-Solving Platforms
Primary Use: Technical interviewing, upskilling, and lifelong learning
Fundamental algorithm and data structure fluency remains critical for career advancement and staying competitive.
Why Algorithms Matter for Your Career:
- Tech screening foundation: Base requirement for most tech interviews
- System design interviewing: Senior/staff roles require distributed systems knowledge
- Problem-solving mindset: Develops computational thinking
- Competitive edge: Differentiates engineers at same seniority level
Top Coding Challenge Platforms:
| Platform | Strengths | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| LeetCode | 2500+ problems, company-specific paths | Interview preparation |
| HackerRank | Gamified learning, real-world assessments | Both learning and hiring |
| Codewars | Community-driven, progressive difficulty | Language mastery |
| Advent of Code | Annual puzzle challenges, community | Recreational learning |
| Project Euler | Mathematical problems, deep thinking | Advanced problem solvers |
Gamified Learning Elements:
- XP and badges: Earn experience points and achievements
- Leaderboards: Competitive ranking by language and difficulty
- Peer solution reviews: Learn alternative approaches
- Streaks: Maintain daily practice momentum
Continuous Learning for Senior Engineers:
- Weekly team challenges: Fun competition with teammates
- Monthly algorithm reviews: Deep dive into specific topics
- System design problems: Practice architectural thinking
- Advanced topics: Distributed systems, consensus algorithms, advanced DP
Comparison Table: Features of Top 10 Essential Developer Tools
| Tool | Core Productivity | AI/Automation | Security | Team Collaboration | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Git & Git-Flow | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Webhooks | ✅ Review rules | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Version control |
| VS Code | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Copilot/Cursor | ✅ Extension support | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Web/polyglot dev |
| IntelliJ IDEA | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Built-in AI | ✅ Plugin ecosystem | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Enterprise/JVM |
| Cursor AI | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Code review assist | ⭐⭐⭐ | Rapid development |
| Builder.io | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Design import | ✅ Permissions | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Frontend/CMS |
| OWASP Toolkit | ⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Automation | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | Security teams |
| Jira | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Automations | ✅ CI/CD gating | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Agile teams |
| Docker | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Container scanning | ✅ Image signing | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | DevOps/Cloud |
| ITIL Tools | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ AI categorization | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Large orgs |
| EQ Platforms | ⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Sentiment AI | ✅ Data privacy | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Remote teams |
| Algorithm Platforms | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ✅ Hint system | ⭐ User accounts | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Interview prep |
Building Your Developer Stack: Best Practices
1. Mixing and Matching Tools for Your Workflow
Select solutions that cater to:
- Team size and distributed vs. co-located setup
- Preferred languages, frameworks, and architectures
- Existing integrations and tech debt
Leverage integrations for seamless context transfer:
- Git ↔ Jira ↔ Slack notifications
- VS Code ↔ Cursor ↔ GitHub Copilot
- Docker ↔ Kubernetes ↔ CI/CD pipelines
Avoid overtooling:
- Favor general-purpose, extensible platforms over best-of-breed point solutions
- Audit quarterly for overlapping tools and redundancy
- Prioritize cross-tool integrations to reduce context switching
2. Optimizing for Your Team's Workflow
Document and share configurations:
- Version control
.vscode/,docker-compose.yml, and IDE settings - Create onboarding checklists for new developers
- Maintain internal wiki with tool best practices
Schedule periodic tool reviews:
- Quarterly check-ins on tool satisfaction
- Annual evaluation of new releases and competitors
- Capture feedback for vendor discussions
3. Continuous Learning and Upskilling
Dedicate time for exploration:
- 2-4 hours per month for experimenting with updates
- Monthly tech talks on tool features and workflows
- Pair programming sessions to share expertise
Build a learning culture:
- Pair senior and junior engineers on new tools
- Host internal demos and workshops
- Celebrate when team members master new tools
4. Avoiding Tool Fatigue and Context Switching
Audit tools for overlap and redundancy:
- Consolidate similar tools (e.g., one project management solution)
- Retire unused tools to reduce cognitive load
- Standardize on ecosystem-specific solutions
Minimize context switching:
- Use IDE integrated terminals (avoid switching to external shell)
- Centralize notifications (avoid checking Slack + Teams + email)
- Use browser extensions to access tools without tab switching
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Guide
Setup and Configuration Challenges
Problem: Version mismatches causing CI/CD failures
Solution: Use Docker containers and containerized development environments to lock versions
Problem: IDE extension conflicts slowing down startup
Solution: Regularly prune unused extensions; use workspace-specific settings; sandbox new tools
Security Missteps to Avoid
❌ Failing to automate security checks in CI/CD pipelines
✅ Solution: Integrate Snyk/Semgrep on every commit, block merges on findings
❌ Ignoring SBOM requirements for compliance
✅ Solution: Generate CycloneDX SBOMs automatically in build pipeline
❌ Neglecting dependency updates
✅ Solution: Use Dependabot/Renovate for automated PR creation
Collaboration Friction Points
❌ Inconsistent Git branching across teams
✅ Solution: Document Git-Flow strategy, enforce via branch protection rules
❌ Missed PRs and notifications from scattered tools
✅ Solution: Centralize notifications; use Slack bots for GitHub/Jira events
People Also Ask (FAQ Section)
Q: What should a developer learn first—Git or an IDE?
A: Git. Version control is fundamental to all modern software development, regardless of language. Master Git basics before diving deep into IDE-specific features.
Q: Can I use free tools instead of paid alternatives?
A: Absolutely. VS Code (free) competes with IntelliJ IDEA. GitHub (free tier) works with most workflows. Many OWASP tools are open-source. Tool cost shouldn't limit mastery.
Q: How long does it take to master these 10 tools?
A: Basic proficiency: 2-3 months; Advanced mastery: 1-2 years. Mastery is continuous—tools evolve constantly.
Q: Should my entire team use the same tools?
A: Core tools (Git, IDE, Docker) should be standardized. Allow flexibility in extension choices. Enforce security and deployment tools across all projects.
Q: How do I keep up with tool updates?
A: Follow official blogs/newsletters, allocate 5-10% of time for learning, automate dependency updates with Dependabot, and schedule quarterly team discussions on new features.
Conclusion
Mastering these 10 essential developer tools arms you with a resilient, scalable, and modern workflow across code management, productivity, security, and collaboration.
The software engineering landscape continues evolving—cloud-first, polyglot, and AI-driven development are now the norm. Success requires building habits of continuous exploration and adaptation. Treat your developer stack as a living asset: documented, discussed, and evolving with team needs.