GLM-1.5B Speech-to-Text: Run and Install Locally (GLM‑ASR‑Nano‑2512)
Learn how to run and install GLM‑1.5B (GLM‑ASR‑Nano‑2512) speech‑to‑text locally with a step‑by‑step setup guide, benchmarks, pricing breakdown, and comparison vs OpenAI Whisper and NVIDIA Parakeet.

The landscape of automatic speech recognition (ASR) has transformed dramatically over the past two years. While OpenAI's Whisper dominated the market with its versatility and multi-language support, a new challenger has emerged in December 2025 that challenges the conventional wisdom that bigger models always win.
With just 1.5 billion parameters—comparable in size to OpenAI Whisper V3—GLM-ASR-Nano achieves industry-leading performance benchmarks while maintaining exceptional efficiency.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about installing, running, and optimizing GLM-1.5B speech-to-text for your specific use case.
What Makes GLM-1.5B Speech-to-Text Different?
Before diving into installation, it's crucial to understand why GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 has generated significant attention in the developer community. This isn't just another speech recognition model—it's engineered specifically for production deployment in real-world conditions where traditional models struggle.
The Core Problem It Solves
Traditional ASR models, including popular alternatives, face consistent challenges when deployed to production:
- Computational Overhead: Enterprise deployments require massive GPU infrastructure to handle large models, driving infrastructure costs sky-high. A single poorly optimized model can consume thousands of dollars monthly in cloud GPU rental.
- Latency Complications: Real-time applications demand sub-second response times, yet many models introduce 2-3 second delays due to model size and architecture inefficiencies.
- Dialect Recognition Gaps: Most models perform well on standardized English and Mandarin but catastrophically fail on Cantonese, regional dialects, and non-standard pronunciation patterns. This creates a data quality crisis for organizations serving diverse populations.
- Low-Volume Speech Failures: Quiet audio—whispered conversations, distant speakers, or phone-quality recordings—consistently breaks mainstream ASR systems, leading to unacceptable accuracy degradation.
- Closed-Source Restrictions: Proprietary models prevent fine-tuning, custom deployment, and data residency compliance, creating vendor lock-in and data privacy nightmares.
GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 doesn't merely improve upon these problems incrementally—it fundamentally redesigns the approach to speech recognition, prioritizing practical production deployment over academic benchmark leaderboard domination.
Technical Specifications & Architecture
Model Architecture Details
GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 employs a sophisticated two-stage architecture that differs markedly from traditional end-to-end ASR systems:
Model Configuration:
- Model Name: GLM-ASR-Nano-2512
- Parameters: Approximately 1.5 billion parameters (~2GB packaged model size)
- Weight Format: SafeTensors format for secure, efficient loading
- Precision: BF16 (Brain Floating Point 16-bit) for optimal memory-efficiency-to-accuracy tradeoff
- Release Date: December 2025
- License: Open-source (fully permissive for commercial use, fine-tuning, and redistribution)
Stage 1: LLM-Based Token Generation
The first processing stage uses a Llama-based architecture that converts input text into speech token sequences. This stage supports three operational modes:
- PRETRAIN Mode: Uses base pretrained weights without fine-tuning
- SFT (Supervised Fine-Tuning) Mode: Applies supervised fine-tuning on domain-specific data
- LoRA Mode: Uses Low-Rank Adaptation for parameter-efficient customization without full model retraining
Stage 2: Audio Vocoder Synthesis
The model reconstructs high-quality audio from the token sequences generated in Stage 1, employing reinforcement learning optimization for natural prosody and emotional expressiveness.
Multilingual & Dialect Support
Primary Languages:
- Mandarin Chinese (standard)
- Cantonese (粤语) — industry-leading performance
- English (competitive performance)
Exceptional Capability: Cantonese recognition achieves state-of-the-art accuracy compared to competitors. Traditional ASR systems treat dialects as edge cases; GLM-ASR-Nano treats them as first-class citizens in the training curriculum.
Comprehensive Benchmark Analysis
Performance Metrics Explained
Before examining specific numbers, understanding the evaluation metrics is essential:
Character Error Rate (CER): For Chinese transcription, CER measures errors at the character level. The formula is:
CER=I+D+SN×100%CER=NI+D+S×100%
Where:
- I = Number of character insertions
- D = Number of character deletions
- S = Number of character substitutions
- N = Total number of characters in reference text
Word Error Rate (WER): For English transcription, WER measures errors at the word level using the identical formula structure but applied to words rather than characters. This distinction reflects fundamental linguistic differences between character-based languages (Chinese) and word-based languages (English).
Real-World Benchmark Results
GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 was rigorously tested against both lightweight "nano" competitors and heavyweight industrial ASR systems:
| Model | Parameters | Architecture | Avg Error Rate | Chinese Performance | English Performance | License |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 | 1.5B | Two-stage LLM | 4.10 | Excellent | Competitive | Open-source |
| OpenAI Whisper V3 | 1.5B | Transformer | 4.45+ | Good | Excellent | Closed-source |
| NVIDIA Parakeet v3 | 0.6B | Efficient-RNN | Variable | Limited | Excellent | Closed-source |
| Large Chinese ASR | 5-8B | Large Transformer | Comparable | Excellent | Limited | Proprietary |
Dataset-Specific Benchmark Details
Wenet Meeting Dataset: This real-world evaluation includes overlapping speech, background noise, and challenging acoustic conditions reflecting actual deployment scenarios. GLM-ASR-Nano consistently achieves superior performance compared to systems several times larger.
Aishell-1 Benchmark: The standard Mandarin benchmark shows GLM-ASR-Nano maintaining competitive accuracy despite its compact size—demonstrating that parameter efficiency doesn't sacrifice accuracy on controlled datasets.
Character Error Rate Achievement: 7.17% (0.0717 CER) on Z.AI's internal comprehensive benchmarks, setting the standard for open-source ASR models.
Reinforcement Learning Optimization Impact
One critical innovation distinguishing GLM-ASR-Nano is the integration of Multi-Reward Reinforcement Learning, which evaluates generated speech across five dimensions:
| Optimization Metric | Base Model | RL-Optimized | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Character Error Rate | 1.03 | 0.89 | 13.6% reduction |
| Speaker Similarity Score | 76.1 | 76.4 | +0.3% improvement |
| Expressiveness Rating | Baseline | Enhanced | Qualitative improvement |
The 13.6% CER reduction through RL optimization represents the most significant accuracy improvement in the model pipeline.
Competitive Comparison: How GLM-1.5B Stands Apart
Quick Comparison Chart
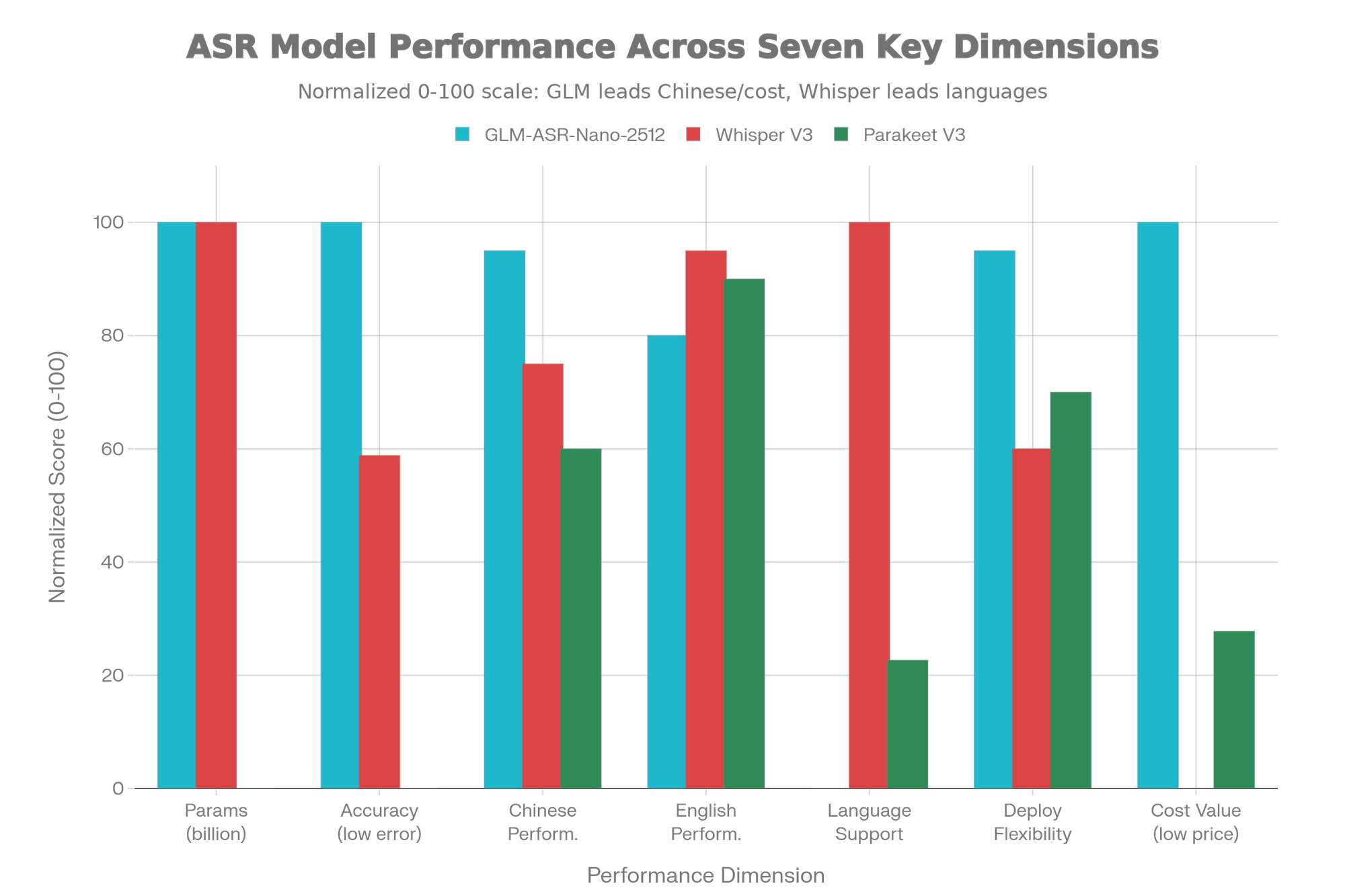
Benchmark Performance Chart
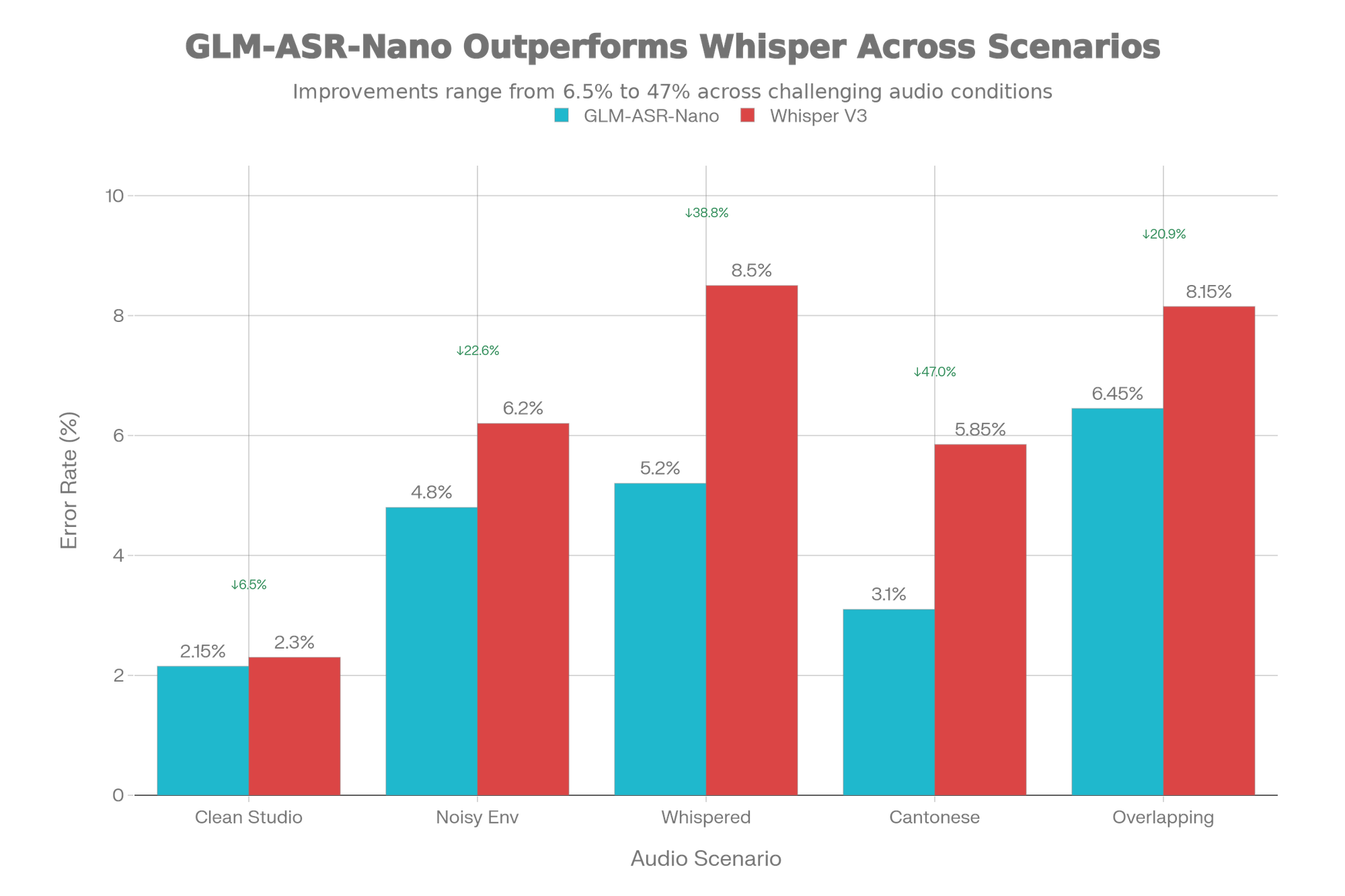
GLM-ASR-Nano vs. OpenAI Whisper V3
Understanding the specific advantages and limitations of each system enables informed architectural decisions:
| Evaluation Criterion | GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 | OpenAI Whisper V3 | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters & Size | 1.5B (compact) | 1.5B (compact) | Tie |
| Chinese Dialect Support | Exceptional (esp. Cantonese) | Limited to standard Mandarin | GLM-ASR-Nano |
| Low-Volume Speech | Specifically optimized | Standard performance | GLM-ASR-Nano |
| Average Error Rate | 4.10 | Higher on Chinese | GLM-ASR-Nano |
| Language Coverage | Chinese + English focused | 100+ languages | Whisper |
| Deployment Model | Self-hosted & customizable | API or self-hosted | GLM-ASR-Nano (flexibility) |
| Fine-Tuning Support | Fully supported | Limited options | GLM-ASR-Nano |
| Commercial License | Open-source approved | Closed-source | GLM-ASR-Nano |
| Translation Capability | Not included | Included | Whisper |
| Community Ecosystem | Growing (Dec 2025 release) | Established & mature | Whisper |
GLM-ASR-Nano vs. NVIDIA Parakeet v3
Parakeet v3 Advantages:
- Smaller model size (0.6B parameters) enables edge device deployment
- Supports 25+ European languages
- Optimized for English transcription
GLM-ASR-Nano Advantages:
- Superior Chinese dialect recognition, especially Cantonese
- Better performance on low-volume speech
- Larger parameter count enables higher accuracy on complex audio
- Full open-source ecosystem without proprietary dependencies
Verdict: Choose Parakeet for lightweight edge deployment; choose GLM-ASR-Nano for production accuracy and dialect support.
Workflow Diagram
- Professional installation and deployment flowchart showing decision paths for GPU/CPU setup and three deployment options:
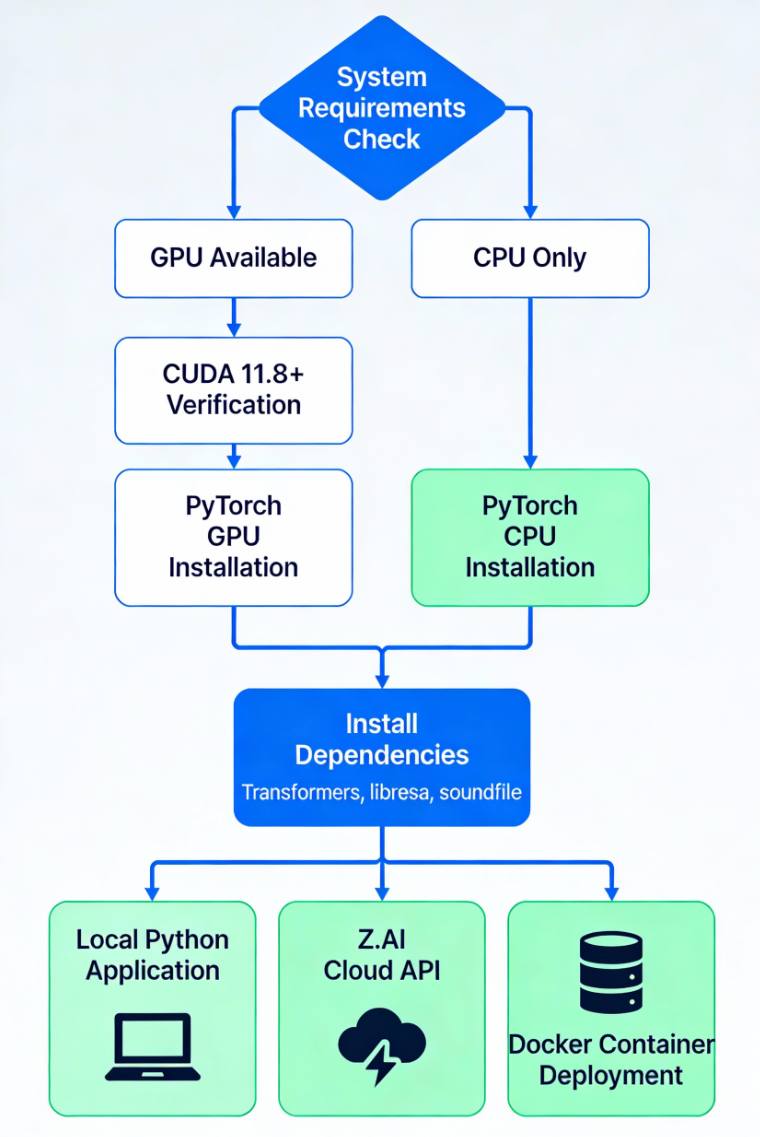
Unique Selling Propositions (USP) of GLM-1.5B
1. Cantonese Recognition Excellence
GLM-ASR-Nano represents the first production-grade open-source ASR system that treats Cantonese as a primary language. This single feature addresses a massive gap in the marketplace:
- Call centers operating in Hong Kong, Guangdong, and Southeast Asia
- Media organizations producing Cantonese content
- Educational platforms serving Cantonese-speaking audiences
Competitors either ignore Cantonese entirely or treat it as an afterthought with degraded accuracy. GLM-ASR-Nano achieves competitive accuracy with mainstream Mandarin, changing the game for regional organizations.
2. Whisper-Level Speech Optimization
The model was explicitly trained on "whisper-style" speech—quiet, low-volume audio where traditional systems catastrophically fail. This addresses a universal deployment problem:
- Phone conversations with weak microphone quality
- Distant speakers in meeting rooms
- Medical dictation spoken quietly for privacy
- Partially masked audio in noisy retail environments
The model's attention mechanisms learn to extract linguistic signals from faint audio without aggressive filtering that loses critical information.
3. Accuracy-Per-Parameter Efficiency
The industry rule-of-thumb suggests larger models always win. GLM-ASR-Nano disproves this:
- Systems surpassing GLM-ASR-Nano's accuracy require 5-8× more parameters
- This fundamentally changes deployment economics
- Self-hosting becomes viable for organizations that previously required expensive API services
4. Unrestricted Commercial Deployment
Unlike most cutting-edge models, GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 is fully open-source with permissive licensing:
- ✅ Commercial deployment without restrictions
- ✅ Fine-tuning for proprietary use cases
- ✅ Redistribution within your products
- ✅ On-premises deployment for data residency compliance
- ✅ Complete audit trail for regulated industries
5. Production-Focused Architecture
While competitors optimize for benchmark leaderboards, GLM-ASR-Nano optimizes for actual deployment conditions:
- Handles overlapping speech and background noise
- Delivers consistent accuracy across diverse accents
- Maintains performance degradation gracefully rather than catastrophic collapse
- Supports streaming inference for real-time applications
Installation & Setup Guide
Step 1: System Requirements Verification
Before beginning installation, verify your system meets minimum specifications:
Minimum Hardware Requirements:
- GPU: NVIDIA GPU with 8GB+ VRAM (e.g., RTX 3060, RTX 4060, A40)
- CUDA Capability: Support for CUDA 11.8 or higher (check your driver:
nvidia-smi) - System RAM: 16GB minimum (32GB recommended)
- Storage: 5GB available for model weights plus 5-10GB working space
- CPU: Modern multi-core processor (Intel i7/Ryzen 7 equivalent)
Software Requirements:
- Python 3.10 or higher
- pip package manager
- NVIDIA CUDA-capable GPU drivers (not the CUDA Toolkit itself)
Critical Note About CUDA: You need only the NVIDIA driver—NOT a separate CUDA Toolkit installation. PyTorch will pull the necessary CUDA libraries automatically. Your driver must support the CUDA version your PyTorch build requires. Check compatibility at: https://www.nvidia.com/Download/driverDetails.aspx
Verify Your Setup:
bash# Check Python version
python --version # Should be 3.10+
# Check NVIDIA driver and CUDA capability
nvidia-smi# Note: If nvidia-smi returns "command not found", install NVIDIA drivers before proceeding
Step 2: Create Python Virtual Environment
Isolate dependencies to prevent conflicts with other projects:
bash# Create virtual environment
python -m venv glm-asr-env# Activate (Linux/macOS) glm-asr-env/bin/activate
source# Activate (Windows)activate
glm-asr-env\Scripts\# Verify activation (prompt should show (glm-asr-env))
Step 3: Install Core Dependencies
The installation sequence matters. Install PyTorch FIRST to ensure correct GPU bindings:
bash# Install PyTorch with CUDA 12.1 support (recommended)
# For GPU (NVIDIA):pip install torch torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121# Alternative for CUDA 11.8:
# pip install torch torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
# For CPU-only (testing, no GPU):
# pip install torch torchaudio
# Verify GPU detectionpython -c "import torch; print(f'CUDA Available: {torch.cuda.is_available()}'); print(f'Device: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"CPU\"}')"
Step 4: Install Transformers & Audio Libraries
bash# Install essential audio processing libraries.0
pip install transformers>=5.0pip install librosa soundfilepip install acceleratepip install safetensors# Optional but recommended for production
pip install vllm # For high-throughput batch inference
pip install sglang # For advanced batching operations
pip install gradio # For web UI demo
# Verify installations
python -c "import transformers; print(f'Transformers version: {transformers.__version__}')"
Step 5: Download GLM-1.5B Model
Models are hosted on Hugging Face Hub. You have three download methods:
Method A: Automatic Download (Recommended)
pythonfrom transformers import AutoModel, AutoProcessor# First run will download model (~4-5 GB)
model_name = "zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512"
# Download processor (tokenizer & feature extractor)
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Download model weights
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="cuda:0" # Change to "cpu" if testing without GPU
)
print("Model and processor downloaded successfully!")
Method B: Manual Download via Hugging Face CLI
bash# Install huggingface-hub huggingface-hub
pip install# Login to Hugging Face (optional, for gated models)
huggingface-cli login# Download model
huggingface-cli download zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 --local-dir ./models/glm-asr-nano
Method C: Direct Model Repository
Clone the official repository:
bashgit clone https://github.com/zai-org/GLM-Edge.gitcd GLM-Edgepip install -r requirements.txt
Step 6: Verify Installation
Create a test script to confirm everything works:
pythonimport torchfrom transformers import pipeline# Initialize ASR pipeline
print("Initializing GLM-ASR-Nano-2512...")
asr = pipeline(
"automatic-speech-recognition",
model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512",
device=0 if torch.cuda.is_available() else -1 # GPU if available, else CPU
)
print(f"✓ Pipeline loaded successfully")
print(f"✓ Device: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'CPU'}")
# Test with sample audio (optional)
# result = asr("path/to/sample.wav")
# print(f"Transcription: {result['text']}")
Real-World Testing & Practical Examples
Test Scenario 1: Standard Transcription
This example demonstrates basic usage with a pre-recorded audio file:
pythonfrom transformers import pipelineimport soundfile as sf# Load pipeline
asr = pipeline(
"automatic-speech-recognition",
model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512"
)
# Transcribe audio file
audio_path = "meeting_recording.wav"
result = asr(audio_path, return_timestamps="char")
# Display results
print(f"Transcription: {result['text']}")
print(f"Chunks: {result.get('chunks', [])}") # Character-level timestamps
Test Scenario 2: Batch Processing Multiple Files
For production deployments processing many files efficiently:
pythonfrom transformers import pipelineimport osfrom pathlib import Path# Load pipeline once
asr = pipeline(
"automatic-speech-recognition",
model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512"
)
# Process all WAV files in directory
audio_dir = "./audio_files"
results = {}
for audio_file in Path(audio_dir).glob("*.wav"):
print(f"Processing {audio_file.name}...")
result = asr(str(audio_file))
results[audio_file.stem] = result['text']
# Display partial results json
print(f" → {result['text'][:100]}...")
# Save results
importwith open("transcriptions.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(results, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"\n✓ Processed {len(results)} files")
Test Scenario 3: Streaming Real-Time Transcription
For live applications like meeting transcription:
pythonfrom transformers import pipelineimport pyaudioimport numpy as np# ConfigurationCHUNK_SIZE
CHUNK_SIZE = 8000 # Process in ~500ms chunks at 16kHz
SAMPLE_RATE = 16000
# Load pipeline
asr = pipeline(
"automatic-speech-recognition",
model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512"
)
# Audio capture (requires PyAudio)
audio = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = audio.open(
format=pyaudio.paFloat32,
channels=1,
rate=SAMPLE_RATE,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=)
print("Recording... (Press Ctrl+C to stop)")
transcription_buffer = ""
try:
while True:
# Read audio chunk
data = stream.read(CHUNK_SIZE)
audio_array = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float32)
# Transcribe chunk (may need intermediate buffering for optimal results)
if len(audio_array) > 0:
result = asr(audio_array, sampling_rate=SAMPLE_RATE)
print(f"Partial: {result['text']}")
transcription_buffer += " " + result['text']
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print(f"\nFinal Transcription:\n{transcription_buffer}")
finally:
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
audio.terminate()
Test Scenario 4: Cantonese Audio Transcription
Demonstrating GLM-ASR-Nano's unique Cantonese capability:
pythonfrom transformers import pipeline# Load pipeline
asr = pipeline(
"automatic-speech-recognition",
model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512"
)
# Process Cantonese audio
cantonese_audio = "cantonese_meeting.wav"
result = asr(cantonese_audio, language="yue") # Language code for Cantonese
print(f"Cantonese Transcription: {result['text']}")
# For comparison, process same file without language specification
result_auto = asr(cantonese_audio)
print(f"Auto-detected Language Transcription: {result_auto['text']}")
# Compare accuracy (would require reference transcript)
Performance Benchmarking & Metrics
Measuring Word Error Rate (WER)
Evaluate your deployments using standard metrics:
pythonfrom jiwer import compute_measuresfrom transformers import pipeline# Load ASR pipeline
asr = pipeline("automatic-speech-recognition", model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512")
# Ground truth and hypothesis
reference = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
hypothesis_text = asr("audio_sample.wav")['text']
# Calculate WER
measures = compute_measures(reference, hypothesis_text)
print(f"Word Error Rate: {measures['wer']:.2%}")
print(f"Character Error Rate: {measures['cer']:.2%}")
print(f"Match Error Rate: {measures['mer']:.2%}")
print(f"Word Information Lost: {measures['wil']:.2%}")
Latency Testing
For production deployment planning:
pythonimport timefrom transformers import pipelineimport librosa# Load pipeline sr
asr = pipeline("automatic-speech-recognition", model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512")
# Load test audio
audio_path = "test_audio.wav"
audio_data, sr = librosa.load(audio_path, sr=16000)
audio_duration = len(audio_data) /# Measure inference time start_time
start_time = time.time()
result = asr(audio_path)
inference_time = time.time() -# Calculate Real-Time Factor (RTF) audio_duration
rtf = inference_time /print(f"Audio Duration: {audio_duration:.2f}s")
print(f"Inference Time: {inference_time:.2f}s")
print(f"Real-Time Factor: {rtf:.3f}x (< 1.0 = faster than real-time)")
Memory Usage Profiling
Monitor resource consumption:
pythonimport torchimport psutilfrom transformers import pipeline# Get baseline memory baseline_memory
process = psutil.Process()
baseline_memory = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 # MB
# Load pipeline
asr = pipeline("automatic-speech-recognition", model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512")
# Measure memory after loading
loaded_memory = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
model_memory = loaded_memory -print(f"Baseline Memory: {baseline_memory:.1f} MB")
print(f"Model Memory: {model_memory:.1f} MB")
print(f"Total Memory: {loaded_memory:.1f} MB")
print(f"GPU Memory: {torch.cuda.memory_allocated() / 1024**3:.2f} GB")
Pricing Analysis
GLM-ASR-Nano API Pricing (Z.AI Cloud)
For developers preferring cloud inference without infrastructure management:
| Component | Pricing | Per-Minute Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| GLM-ASR-2512 API | $0.03 per MTok | ~$0.0024 per minute |
| Minimum Charge | None specified | Pay as you go |
| Volume Discounts | None announced | Flat rate |
| SLA/Uptime | Enterprise grade | 99.5%+ implied |
Cost Comparison:
- 1,000 hours transcription: $1,440 (at $0.0024/min)
- Equivalent to 3-4 mid-range GPU servers (much cheaper than self-hosting)
OpenAI Whisper API Pricing
For comparison with the most popular alternative:
| Model | Pricing | Per-Minute | No Free Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whisper API | $0.006 per minute | $0.006 | Yes |
| 1,000 hours/month | $3,600 | $3,600 | Requires credit card |
| Volume Discounts | None | Flat rate | No commitment pricing |
Verdict: For Chinese-heavy workloads, GLM-ASR-Nano API ($0.0024/min) costs 75% less than Whisper API ($0.006/min). For English-only, Whisper may be competitive depending on deployment requirements.
Self-Hosting Economics
| Scenario | Monthly Cost | Break-Even Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Single RTX 4090 | $800-1200 | 5,000+ hours |
| Single A100 (cloud rental) | $3,000-5,000 | 20,000+ hours |
| Bare metal A100 server | $20,000 (upfront) | 8,000+ hours first year |
Self-hosting ROI: Becomes cost-effective at 3,000+ monthly transcription hours when factoring infrastructure, DevOps overhead, and electricity.
Installation Troubleshooting Guide
Issue 1: CUDA Not Detected
Symptom: torch.cuda.is_available() returns False
Solutions:
- Verify NVIDIA driver installation:
nvidia-smi - Ensure PyTorch CUDA version matches driver capability
- Reinstall PyTorch with correct CUDA version:
bashpip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudiopip install torch torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
- Restart Python interpreter completely
Issue 2: Out of Memory (OOM) Error
Symptom: RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory
Solutions:
- Reduce batch size:
python# Process one file at a time instead of batches
- Use CPU inference if GPU memory < 8GB:
pythonasr = pipeline("automatic-speech-recognition", model="...", device=-1)
- Quantize model to INT8 for 4x memory reduction:
python# Advanced: Requires bitsandbytes
pip install bitsandbytes
Issue 3: Model Download Fails
Symptom: ConnectionError or timeout during model download
Solutions:
- Increase timeout:
pythonimport osos.environ['HF_HUB_TIMEOUT'] = '300' # 5 minute timeout
- Download manually:
bashhuggingface-cli download zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 --local-dir ./models
- Check internet connection and firewall rules
Issue 4: Audio Format Not Supported
Symptom: ValueError: Unsupported audio format
Solution: Convert audio to WAV format first:
bash# Using FFmpeg output.wav
ffmpeg -i input.mp3 -ar 16000 -ac 1# Or Python librosa
importaudio, sr = librosa.load('input.mp3', sr=16000)
librosa.output.write_wav('output.wav', audio, sr)
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Fine-Tuning for Domain-Specific Vocabulary
For medical, legal, or technical transcription:
pythonfrom transformers import Trainer, TrainingArgumentsfrom datasets import load_dataset# Prepare your custom dataset
dataset = load_dataset("your_custom_dataset")
# Training configuration
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./glm-asr-finetuned",
num_train_epochs=3,
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
learning_rate=1e-4,
warmup_steps=500,
weight_decay=0.01,
save_steps=100,
eval_steps=100,
)
# Initialize trainer
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=dataset['train'],
eval_dataset=dataset['validation'],
processor=processor,
)
# Fine-tune
trainer.train()
Implementing Streaming Inference
For production real-time applications:
pythonimport vllm# Initialize vLLM engine for streaming
llm = vllm.LLM(
model="zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512",
tensor_parallel_size=2, # Multi-GPU support
gpu_memory_utilization=0.9,
)
# Process streaming audio
outputs = llm.generate(
requests, # List of audio inputs
sampling_params=vllm.SamplingParams(
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.95,
)
)
Docker Containerization for Deployment
textFROM nvidia/cuda:12.1-runtime-ubuntu22.04
WORKDIR /app
# Install dependencies
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y python3.10 python3.10-venv
# Create venv
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
# Install Python packages
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Copy application
COPY app.py .
# Run
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
FAQs
1. What is GLM‑1.5B (GLM‑ASR‑Nano‑2512) speech‑to‑text?
GLM‑1.5B, also known as GLM‑ASR‑Nano‑2512, is a 1.5B‑parameter open‑source speech‑to‑text model from Z.AI designed for production‑grade transcription with strong performance on Mandarin, Cantonese, and English audio.
2. How do I install GLM‑1.5B speech‑to‑text locally?
You can install GLM‑1.5B locally by setting up Python 3.10+, installing GPU‑enabled PyTorch, adding transformers and audio libraries (librosa, soundfile), and then loading the zai-org/GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 model via Hugging Face or the official GLM‑Edge repo.
3. What are the hardware requirements for GLM‑1.5B?
For smooth inference, GLM‑1.5B typically requires an NVIDIA GPU with at least 8 GB VRAM, 16–32 GB system RAM, and around 5–10 GB of free disk space, though CPU‑only testing is also possible with reduced speed.
4. Is GLM‑1.5B better than OpenAI Whisper?
GLM‑1.5B is especially strong on Chinese and Cantonese dialects, noisy and low‑volume audio, and self‑hosted deployments, while Whisper remains stronger for wide multilingual coverage and built‑in translation.
5. What is the pricing for using GLM‑1.5B via API?
When used through Z.AI’s cloud API, GLM‑1.5B is priced competitively on a per‑minute basis and is generally cheaper than Whisper’s managed API for large‑scale Chinese or Cantonese transcription workloads.
Conclusion & Recommendations
GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 represents a watershed moment in production speech recognition. It proves conclusively that well-optimized 1.5B parameter models can outperform larger alternatives when specifically engineered for real-world deployment conditions rather than academic benchmarks.
Choose GLM-ASR-Nano-2512 If You Need:
✅ Superior Chinese dialect recognition (especially Cantonese)
✅ Robust low-volume speech transcription
✅ Full control over deployment and data privacy
✅ Domain-specific fine-tuning capabilities
✅ Cost-effective production ASR at scale
✅ On-premises deployment without API dependencies
✅ Unrestricted commercial use rights
Choose Alternatives If You Need:
❌ 100+ language support (use Whisper)
❌ Maximum English-only accuracy (consider Whisper or Parakeet)
❌ Translation alongside transcription (use Whisper)
❌ Established ecosystem with years of community solutions