GLM-4.6 vs Qwen3-Max 2025: Comparison & Performance Analysis
GLM-4.6 vs Qwen3-Max detailed comparison: benchmark results, pricing analysis, technical specs, and performance testing. Discover which trillion-parameter AI model leads in 2025.

The battle for AI supremacy has intensified with two flagship Chinese language models competing at the cutting edge of artificial intelligence: GLM-4.6 from Zhipu AI (Z.ai) and Qwen3-Max from Alibaba.
Both models represent significant achievements in large language model development, offering distinct approaches to solving complex reasoning, coding, and agentic tasks while establishing China as a formidable force in the global AI landscape.
Summary
GLM-4.6 emerges as the cost-effective, open-source champion with exceptional mathematical reasoning capabilities and competitive coding performance, while Qwen3-Max positions itself as the trillion-parameter powerhouse optimized for enterprise-scale applications and multi-turn reasoning tasks.
Technical Architecture and Specifications
GLM-4.6: Efficient MoE Design
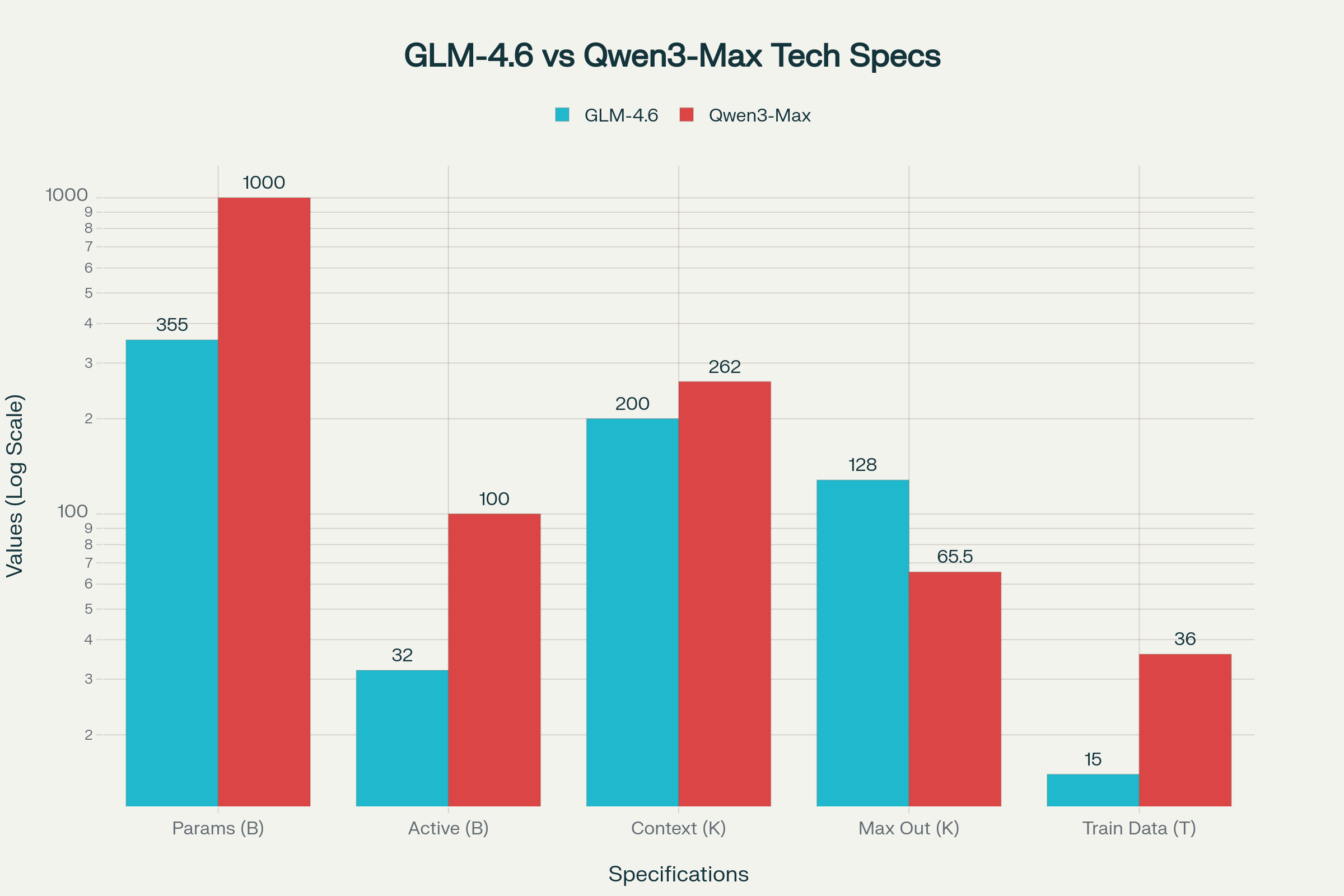
GLM-4.6 utilizes a 355-billion parameter Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture with 32 billion active parameters per forward pass. This design choice prioritizes computational efficiency while maintaining high performance across diverse tasks. The model's architecture represents an evolution from GLM-4.5, incorporating enhanced training stability and improved token efficiency.
The model supports a 200K token context window, expanded from the previous generation's 128K limit, enabling more complex agentic workflows and document processing tasks. With a maximum output capacity of 128K tokens, GLM-4.6 can generate substantial content while maintaining coherence across extended sequences.
Qwen3-Max: Trillion-Parameter Scale
Qwen3-Max crosses the one trillion parameter threshold, making it one of the largest production-ready language models available. The model employs a sophisticated MoE design with sparse activation patterns, allowing efficient inference despite its massive scale. Trained on an unprecedented 36 trillion tokens of multilingual data, Qwen3-Max represents a significant leap in training scale compared to its predecessors.
The model offers a 262K token context window, providing superior long-document processing capabilities compared to GLM-4.6. However, its maximum output is limited to 65.5K tokens, focusing on quality over quantity in generation tasks.
Benchmark Performance Analysis
Mathematical Reasoning Excellence
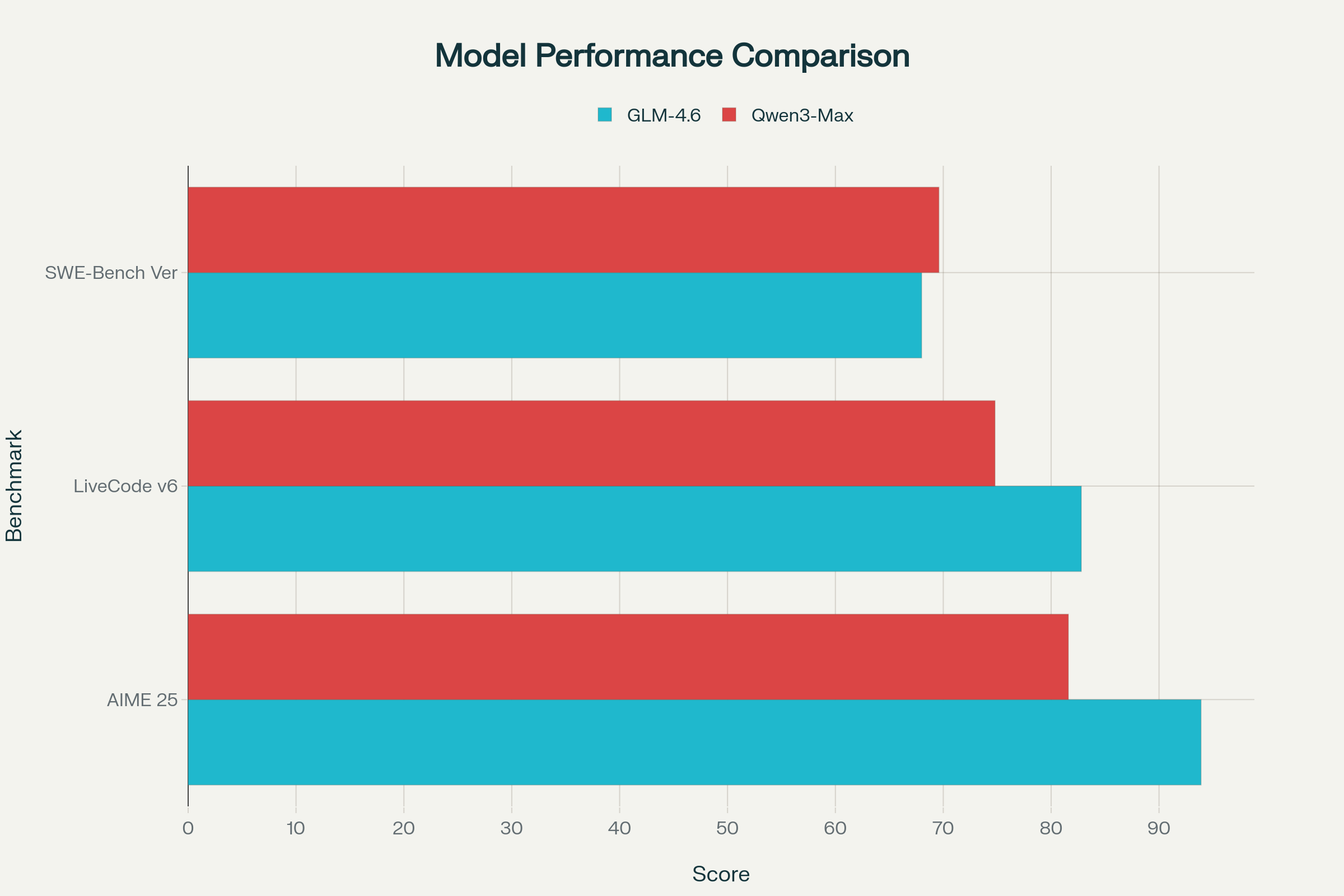
GLM-4.6 demonstrates exceptional mathematical capabilities, achieving 93.9% on AIME 25, significantly outperforming Qwen3-Max's 81.6%. This represents one of the highest scores recorded on this challenging mathematical reasoning benchmark, indicating GLM-4.6's superior ability to handle complex multi-step mathematical problems.
Coding Proficiency
In coding benchmarks, GLM-4.6 maintains a competitive edge with 82.8% on LiveCodeBench v6 compared to Qwen3-Max's 74.8%. However, the competition tightens in real-world software engineering tasks, where Qwen3-Max slightly edges ahead with 69.6% on SWE-Bench Verified versus GLM-4.6's 68.0%.
Multi-Turn Reasoning and Agent Tasks
Qwen3-Max excels in complex reasoning scenarios, achieving 86.1% on Arena-Hard v2, a benchmark designed to evaluate multi-turn conversational abilities and complex instruction following. The model also demonstrates strong performance on Tau2-Bench Verified (72.5%) and LiveBench (79.3%), indicating robust capabilities across diverse task types.
Real-World Performance Testing
Coding Integration and Developer Experience
Both models have been extensively tested in real-world development environments. GLM-4.6 shows near parity with Claude Sonnet 4 in practical coding tasks, achieving a 48.6% win rate in head-to-head comparisons using the CC-Bench evaluation framework. Developers report that GLM-4.6 generates more polished front-end code with better visual aesthetics compared to its predecessors.
The model successfully integrates with popular coding tools including Claude Code, Cline, Roo Code, and Kilo Code, demonstrating its versatility in developer workflows. Token efficiency improvements of approximately 15% compared to GLM-4.5 make it more cost-effective for extended coding sessions.
Enterprise Agent Capabilities
Qwen3-Max showcases superior agent capabilities through its thinking and non-thinking modes, allowing users to balance computational cost with reasoning depth. The model's production-ready thinking mode enables sophisticated tool-augmented workflows, making it particularly suitable for enterprise applications requiring autonomous task execution.
The model's extensive multilingual support covering 119 languages and dialects positions it favorably for global enterprise deployments. Its robust performance across diverse benchmarks indicates reliability in varied operational contexts.
Cost Analysis and Accessibility
Pricing Comparison
GLM-4.6 offers significantly more affordable access through Z.ai's official API at $0.60 per million input tokens and $2.20 per million output tokens. This pricing strategy makes it approximately three times cheaper than comparable models, addressing a critical barrier to AI adoption for smaller organizations and developers.
Qwen3-Max pricing varies by region, with Alibaba Cloud Singapore charging $1.20 input/$6.00 output per million tokens, while Beijing pricing offers better rates at $0.861 input/$3.441 output. The model's proprietary nature means access is limited to Alibaba's ecosystem and select API providers.
Open Source vs Proprietary
GLM-4.6's MIT license open-source availability represents a significant advantage for organizations requiring full control over their AI infrastructure. This approach enables local deployment, customization, and integration without vendor lock-in concerns.
Qwen3-Max remains proprietary, limiting deployment options to cloud-based APIs. While this approach ensures consistent performance and support, it creates dependencies on Alibaba's infrastructure and pricing decisions.
Multilingual and Safety Considerations
Language Support
Both models demonstrate strong multilingual capabilities, with Qwen3-Max supporting 119 languages and dialects while GLM-4.6 shows competitive performance across major languages. The extensive training data for both models includes diverse linguistic content, enabling effective cross-language understanding and generation.
Safety and Alignment
GLM-4.6 benefits from enhanced natural language alignment through reinforcement learning and preference optimization, delivering smoother conversational flow and better style matching. The model demonstrates improved safety characteristics while maintaining creative capabilities.
Qwen3-Max incorporates comprehensive safety measures developed through Alibaba's extensive testing protocols. The model's thinking mode includes built-in reasoning safeguards to prevent harmful outputs during complex reasoning tasks.
Use Case Recommendations
When to Choose GLM-4.6
- Budget-conscious projects requiring high-quality AI capabilities without premium pricing
- Open-source deployment needs with full control over model infrastructure
- Mathematical and scientific applications where reasoning precision is paramount
- Development workflows requiring efficient coding assistance and front-end generation
- Organizations seeking vendor independence and customization capabilities
When to Choose Qwen3-Max
- Enterprise-scale applications requiring maximum model capability and reliability
- Complex agent workflows with sophisticated tool integration requirements
- Multilingual global deployments needing comprehensive language support
- Long-document processing tasks exceeding 200K token contexts
- Organizations comfortable with cloud-based AI services and proprietary models
Performance Optimization and Deployment
GLM-4.6 Optimization
Local deployment of GLM-4.6 requires substantial hardware resources, with optimal performance achieved using 205GB unified memory or combined RAM+VRAM for acceptable generation speeds. The model supports various quantization techniques including KV cache quantization to reduce memory requirements while maintaining performance quality.
Community implementations through llama.cpp and other frameworks enable efficient deployment across diverse hardware configurations. The model's MoE architecture allows for strategic quantization of inactive experts, significantly reducing deployment costs.
Qwen3-Max Scaling
Qwen3-Max's cloud-native design eliminates deployment complexity while ensuring consistent performance. The model's sparse activation patterns in its MoE architecture enable efficient scaling across Alibaba's infrastructure, supporting concurrent user access without degradation.
API-based access provides predictable latency and throughput characteristics, with 29.7 tokens per second average speed and 1.67-second time to first token. These metrics position it competitively for production applications requiring reliable response times.
Future Development Trajectory
GLM-4.6 Evolution
Zhipu AI continues developing the GLM series with focus on improved efficiency and broader accessibility. The company's commitment to open-source development suggests future versions will maintain this philosophy while incorporating advanced capabilities from proprietary research.
The GLM Coding Plan subscription service starting at $3/month indicates a hybrid business model balancing open-source availability with premium services for developers.
Qwen3-Max Roadmap
Alibaba's investment in the Qwen3 ecosystem includes ongoing development of specialized variants including vision-language models and domain-specific implementations. The company's focus on enterprise adoption suggests continued enhancement of agent capabilities and tool integration features.
The introduction of Qwen3-Max-Thinking variants indicates advancement toward more sophisticated reasoning capabilities, potentially challenging OpenAI's reasoning models in future iterations.
Industry Impact and Adoption
Chinese AI
Both models exemplify China's growing competitiveness in the global AI landscape, with Chinese companies leading in GenAI usage at 83% adoption rates compared to other regions. This domestic adoption provides valuable feedback for model improvement and real-world validation.
The success of GLM-4.6 and Qwen3-Max demonstrates China's capability to develop competitive alternatives to Western AI models, potentially reshaping global AI supply chains and reducing dependence on foreign technology.
Global Implications
The aggressive pricing and performance characteristics of these models are driving industry-wide cost reductions and accelerating AI democratization. This trend benefits global users through increased accessibility and competitive pressure on established providers.
The emergence of viable alternatives to GPT and Claude models creates opportunities for diversified AI strategies among enterprises, reducing vendor lock-in risks and enabling more competitive procurement processes.
Comparative Analysis Summary
Performance Leadership
GLM-4.6 excels in mathematical reasoning and cost efficiency, making it ideal for budget-conscious applications requiring precise analytical capabilities. Its open-source nature and competitive coding performance position it as an attractive alternative for development-focused workflows.
Qwen3-Max dominates in scale and enterprise readiness, offering superior context handling and multi-turn reasoning capabilities. Its comprehensive language support and sophisticated agent features make it suitable for large-scale, international deployments.
Strategic Positioning
The competition between these models reflects broader strategic differences in AI development philosophy. GLM-4.6's open-source approach prioritizes accessibility and community development, while Qwen3-Max's proprietary model focuses on enterprise reliability and controlled access.
Both approaches offer compelling value propositions, with the optimal choice depending on specific organizational requirements, technical constraints, and strategic objectives. The continued development of both model families ensures ongoing innovation and competitive pressure in the AI market.
Technical Implementation Considerations
Integration Complexity
GLM-4.6's open-source nature enables deep integration with existing systems while requiring more technical expertise for optimal deployment. Organizations must consider infrastructure costs and maintenance overhead against the benefits of full control and customization capabilities.
Qwen3-Max's API-based access simplifies integration but creates dependencies on Alibaba's infrastructure and service reliability. The model's comprehensive documentation and enterprise support features offset some complexity concerns for business users.
Performance Monitoring
Both models require careful performance monitoring in production environments. GLM-4.6's local deployment enables detailed performance analysis and optimization, while Qwen3-Max's cloud-based nature relies on Alibaba's monitoring and optimization capabilities.
The choice between these approaches depends on organizational capabilities, compliance requirements, and performance optimization needs specific to each use case.
Conclusion
The competition between GLM-4.6 and Qwen3-Max represents a pivotal moment in AI development, showcasing China's capability to develop world-class language models that compete directly with established Western alternatives.
GLM-4.6's combination of open-source accessibility, mathematical excellence, and cost efficiency makes it an compelling choice for organizations prioritizing flexibility and budget considerations.
Meanwhile, Qwen3-Max's trillion-parameter scale, enterprise features, and comprehensive capabilities position it as a premium solution for large-scale applications requiring maximum performance and reliability.