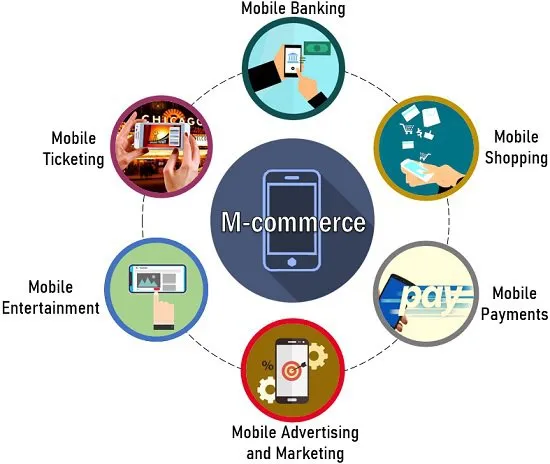
Most Important M-Commerce Applications

M-Commerce (Mobile Commerce) is reshaping how people shop, bank, and interact with businesses. As smartphones become an integral part of our daily lives, businesses are leveraging mobile platforms to enhance customer experiences and drive sales.
What is M-Commerce?
M-Commerce, deals with buying and selling of goods and services through smartphones, tablets etc using digital transactions. It doesn’t require physical contact between two people for sending or receiving the money.
Here are some key applications of m-commerce:
1. Retail and E-Commerce
- Mobile Shopping: Consumers can browse and purchase products from online stores using mobile apps or websites (e.g., Amazon, eBay, Shopify).
- In-App Purchases: Apps like fashion retailers (e.g., Zara, ASOS) allow users to buy products directly within the app.
- Personalised Recommendations: AI-driven suggestions based on user behaviour and preferences.
2. Mobile Payments
- Digital Wallets: Services like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay enable contactless payments using smartphones.
- Peer-to-Peer Payments: Apps like Venmo, PayPal, and Cash App allow users to send and receive money instantly.
- QR Code Payments: Popular in Asia, apps like Alipay and WeChat Pay use QR codes for seamless transactions.
3. Banking and Financial Services
- Mobile Banking: Apps from banks (e.g., Chase, Bank of America) allow users to check balances, transfer funds, and pay bills.
- Investment Platforms: Apps like Robinhood and Acorns enable users to trade stocks and manage investments on the go.
- Cryptocurrency Trading: Platforms like Coinbase and Binance allow users to buy, sell, and manage cryptocurrencies.
4. Food Delivery and Restaurants
- Food Delivery Apps: Services like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub let users order food from local restaurants.
- Table Reservations: Apps like OpenTable allow users to book tables at restaurants.
- Mobile Menus: Restaurants use QR codes to display digital menus, reducing physical contact.
5. Travel and Hospitality
- Booking Platforms: Apps like Expedia, Booking.com, and Airbnb allow users to book flights, hotels, and vacation rentals.
- Mobile Check-In: Airlines and hotels offer mobile check-in options to streamline the process.
- Travel Guides: Apps like TripAdvisor provide recommendations and reviews for travelers.
6. Ride-Hailing and Transportation
- Ride-Hailing Services: Apps like Uber, Lyft, and Grab allow users to book rides and pay through their smartphones.
- Public Transit: Apps like Citymapper and Moovit provide real-time transit information and mobile ticketing.
- Car Rentals: Platforms like Turo and Zipcar enable users to rent vehicles via mobile apps.
7. Healthcare and Wellness
- Telemedicine: Apps like Teladoc and Amwell allow patients to consult with doctors remotely.
- Fitness Apps: Platforms like MyFitnessPal and Fitbit track health metrics and offer personalised workout plans.
- Pharmacy Services: Apps like CVS and Walgreens allow users to order prescriptions and manage medications.
8. Entertainment and Media
- Streaming Services: Apps like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube offer on-demand entertainment.
- In-App Purchases: Mobile games and apps offer virtual goods, subscriptions, and premium features.
- Event Ticketing: Apps like Ticketmaster and Eventbrite allow users to purchase and store tickets on their phones.
9. Social Commerce
- Shoppable Posts: Platforms like Instagram and Pinterest allow users to buy products directly from posts.
- Live Shopping: Apps like Taobao Live and Facebook Live enable real-time product demonstrations and purchases.
- Influencer Marketing: Brands collaborate with influencers to promote products via social media.
10. Education and E-Learning
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer mobile-friendly courses.
- Language Learning: Apps like Duolingo and Babbel provide interactive language lessons.
- Virtual Classrooms: Apps like Zoom and Google Classroom facilitate remote learning.
11. Real Estate
- Property Listings: Apps like Zillow and Realtor.com allow users to search for homes and apartments.
- Virtual Tours: Real estate agents use mobile apps to offer virtual property tours.
- Mortgage Calculators: Apps help users estimate mortgage payments and compare loan options.
12. Gaming
- Mobile Games: Games like Candy Crush and PUBG Mobile generate revenue through in-app purchases and ads.
- Cloud Gaming: Services like Xbox Cloud Gaming and NVIDIA GeForce Now allow users to stream games on mobile devices.
- Esports Betting: Apps enable users to place bets on esports tournaments.
13. Logistics and Supply Chain
- Delivery Tracking: Apps like FedEx and UPS allow users to track packages in real-time.
- Fleet Management: Businesses use mobile apps to monitor and optimize delivery routes.
- Inventory Management: Retailers use mobile tools to manage stock levels and orders.
14. Nonprofits and Fundraising
- Donation Apps: Platforms like GoFundMe and Charity Navigator enable users to donate to causes via mobile devices.
- Crowdfunding: Apps like Kickstarter and Indiegogo allow users to support projects and startups.
15. Government and Public Services
- Mobile Voting: Some regions are experimenting with mobile voting for elections.
- Public Service Apps: Governments use apps to provide information, process payments (e.g., taxes, fines), and offer emergency alerts.
- Digital IDs: Mobile apps store digital versions of identification documents (e.g., driver’s licenses).
16. Augmented Reality (AR) Shopping
- Virtual Try-Ons: Apps like Sephora and IKEA use AR to let customers try on makeup or visualise furniture in their homes.
- Interactive Ads: Brands use AR to create engaging advertisements that allow users to interact with products.
17. Subscription Services
- Streaming Subscriptions: Apps like Netflix, Spotify, and Disney+ offer monthly subscriptions for content.
- Meal Kits: Services like HelloFresh and Blue Apron deliver meal kits based on mobile orders.
- Fitness Memberships: Apps like Peloton and ClassPass offer subscription-based fitness classes.
18. Smart Home and IoT Integration
- Mobile Control: Apps like Google Home and Amazon Alexa allow users to control smart home devices remotely.
- IoT Payments: Mobile devices can be used to pay for connected services, such as electric vehicle charging.
19. Agriculture and Farming
- Farm Management Apps: Farmers use mobile apps to monitor crops, manage equipment, and track weather conditions.
- Marketplace Apps: Platforms connect farmers directly with buyers for produce and livestock.
20. Automotive Industry
- Car Buying Apps: Platforms like Carvana and AutoTrader allow users to buy and sell vehicles online.
- Connected Cars: Apps enable users to control car features (e.g., locking doors, starting engines) remotely.
Advantages or Pros of M-Commerce
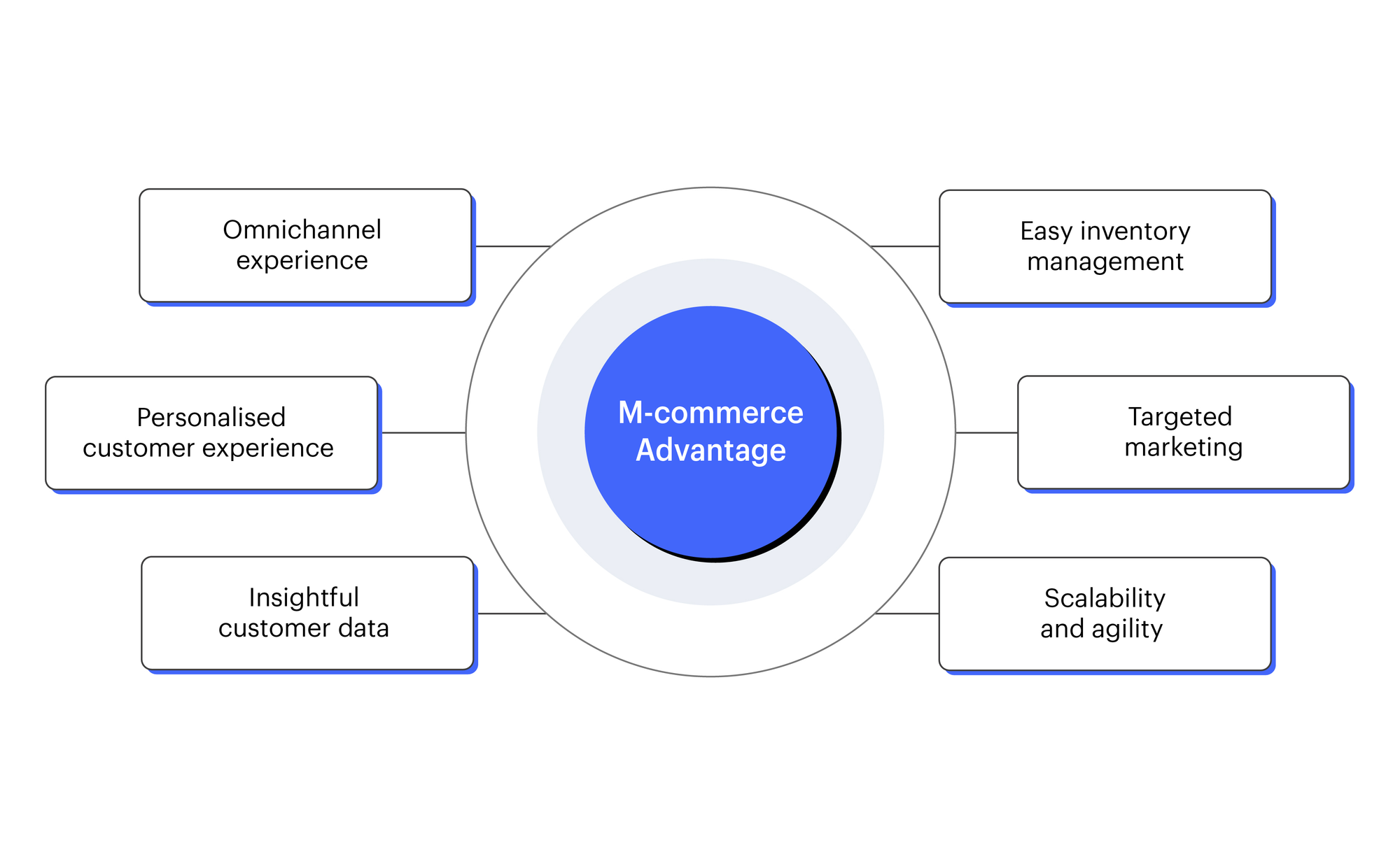
- Increases the amount of customer retention.
- Wider variety of commodities and services.
- More options for selecting the product.
- Convenient for the consumer to compare the pricing, product reviews and make purchases.
- Multiple options for payments like credit card, debit card payments, UPI, internet banking etc.
- Better user experience.
- Convenience and accessibility.
- Faster transactions.
- Personalised shopping experience through AI and analytics.
- Widens businesses reach.
Disadvantages or Cons of M-Commerce

- Initial cost of M-commerce begin a business is high.
- Poor network strength and low bandwidth speed.
- Security and privacy risk.
- Poor designed app can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
- Mobile payment is still not available across many locations in the world.
- Device compatibility issue.
- Limited screen size hampers proper product viewing.
- Limited digital literacy.
- Fraud websites and apps discourages customers.
- Advertisers spamming.
Conclusion
M-commerce is transforming industries by making transactions faster, more convenient, and accessible. As mobile technology continues to evolve, its applications will expand further, creating new opportunities for businesses and consumers alike.